The Fibonacci sequence is a series of numbers where a number is found by adding up the two numbers before it. Starting with 0 and 1, the sequence goes 0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 34, and so forth. Written as a rule, the expression is xn = xn-1 + xn-2.
Named after Fibonacci, also known as Leonardo of Pisa or Leonardo Pisano, Fibonacci numbers were first introduced in his Liber abaci in 1202. The son of a Pisan merchant, Fibonacci traveled widely and traded extensively. Math was incredibly important to those in the trading industry, and his passion for numbers was cultivated in his youth.
Knowledge of numbers is said to have first originated in the Hindu-Arabic arithmetic system, which Fibonacci studied while growing up in North Africa. Prior to the publication of Liber abaci, the Latin-speaking world had yet to be introduced to the decimal number system. He wrote many books about geometry, commercial arithmetic and irrational numbers. He also helped develop the concept of zero.
The first 21 Fibonacci numbers Fn for n = 0, 1, 2, …, 20 are:
F0 F1 F2 F3 F4 F5 F6 F7 F8 F9 F10 F11 F12 F13 F14 F15 F16 F17 F18 F19 F20 0 1 1 2 3 5 8 13 21 34 55 89 144 233 377 610 987 1597 2584 4181 6765
The sequence can also be extended to negative index n using the re-arranged recurrence relation
which yields the sequence of "negafibonacci" numbers satisfying
Thus the bidirectional sequence is
F−8 F−7 F−6 F−5 F−4 F−3 F−2 F−1 F0 F1 F2 F3 F4 F5 F6 F7 F8 −21 13 −8 5 −3 2 −1 1 0 1 1 2 3 5 8 13 21
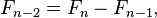

No comments:
Post a Comment